Increased Adoption by Institutional Investors
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the adoption of cryptocurrencies by institutional investors. This is due to a number of factors, including the growing acceptance and legitimacy of cryptocurrencies as an asset class, as well as the potential for high returns.
One of the main drivers of institutional adoption has been the emergence of regulated cryptocurrency exchanges and custodians, which provide a secure and transparent way for institutions to invest in cryptocurrencies. These platforms comply with the same regulatory requirements as traditional financial institutions, and provide robust security measures to protect against fraud and theft.

Another factor driving institutional adoption is the growing demand from investors for exposure to cryptocurrencies. As more individuals and retail investors have begun to invest in cryptocurrencies, institutional investors have also begun to take notice and consider adding cryptocurrencies to their portfolios in order to meet this demand.
Institutional adoption has also been facilitated by the development of a range of financial instruments and products that allow institutions to invest in cryptocurrencies in a way that meets their specific needs and risk profiles. For example, some institutional investors have invested in Bitcoin futures contracts or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the performance of cryptocurrencies.
Overall, the increased adoption of cryptocurrencies by institutional investors is a positive development for the industry, as it brings greater stability and legitimacy to the market. It also provides a significant source of liquidity and demand for cryptocurrencies, which can help to drive prices higher over the long-term.
Mainstream Acceptance
Mainstream acceptance refers to the widespread acceptance and integration of an idea, product, or practice into mainstream society or culture. This means that the idea or product is no longer seen as unusual, unconventional, or out of the ordinary, but rather as a common and accepted part of everyday life.

Achieving mainstream acceptance often requires overcoming significant resistance or barriers, as new or innovative ideas may face skepticism, opposition, or even ridicule before gaining wider acceptance. However, once an idea or product becomes mainstream, it often becomes easier to promote and market, as it no longer faces the same level of resistance or pushback.
Examples of ideas or products that have achieved mainstream acceptance include the internet, social media, smartphones, electric cars, and renewable energy. Each of these innovations faced initial resistance or skepticism, but they eventually became ubiquitous and widely adopted by society.
Regulatory Clarity
Regulatory clarity refers to a clear and well-defined regulatory framework that governs a particular industry or sector. It means that regulations are unambiguous, consistent, and easy to understand, making it easier for businesses to comply with them.
Regulatory clarity is important because it provides businesses with a level of certainty and predictability that they need to operate and invest in a particular market. It also promotes fair competition and helps prevent regulatory arbitrage, where companies exploit regulatory loopholes to gain an unfair advantage.

When regulations are clear, businesses can make informed decisions about how to operate and innovate in the market without fear of running afoul of the law. This encourages entrepreneurship and innovation, which can drive economic growth and create jobs.
In contrast, a lack of regulatory clarity can create uncertainty, increase compliance costs, and discourage investment in a particular market. This can stifle innovation and economic growth, as businesses are hesitant to take risks when the regulatory environment is unclear.
Overall, regulatory clarity is important for promoting economic growth, innovation, and fair competition. It helps businesses understand what is expected of them, allowing them to make informed decisions and compete on a level playing field.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) refers to a new financial system that is built on blockchain technology, which enables financial transactions and services to be conducted in a decentralized, open-source, and permissionless manner, without the need for intermediaries such as banks or other financial institutions.
DeFi applications are built on top of decentralized blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, and use smart contracts to automate financial transactions and eliminate the need for intermediaries. This enables users to access a range of financial services, such as lending, borrowing, trading, and investing, in a decentralized and transparent manner.

Some of the most popular DeFi applications include decentralized exchanges (DEXs), which enable peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies, and lending platforms, which allow users to borrow and lend cryptocurrencies without the need for a centralized intermediary. Other DeFi applications include prediction markets, insurance, stablecoins, and more.
The growth of DeFi has been explosive in recent years, with the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi applications reaching over $200 billion in 2021. However, the DeFi space is still relatively new and unregulated, and there are risks associated with using DeFi applications, such as smart contract bugs, market volatility, and the potential for hacks or attacks.
NFTs
NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, are digital assets that are stored on a blockchain. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, which are fungible and interchangeable with one another, each NFT is unique and represents a specific digital item, such as a piece of art, a video game item, or a tweet.

NFTs are created using smart contracts on blockchain platforms such as Ethereum, and are bought and sold on NFT marketplaces. The ownership and authenticity of NFTs are verified through blockchain technology, which ensures that they are not duplicated or counterfeited.
The popularity of NFTs has exploded in recent years, with some selling for millions of dollars. Some see NFTs as a way for artists and creators to monetize their digital creations in a way that was previously impossible. However, there are also concerns about the environmental impact of NFTs, as the energy required to mint and trade them can be significant.
Interoperability
Interoperability is the ability of different computer systems, devices, or software applications to communicate and exchange data with each other. In other words, it is the capability of different systems to work together seamlessly and efficiently.

Interoperability is critical in today’s technology-driven world, where various devices and applications need to communicate with each other to perform complex tasks. For example, a smartphone needs to be able to communicate with a wireless network, access various applications, and exchange data with other devices such as laptops, tablets, and wearable devices.
In healthcare, interoperability is crucial for the exchange of electronic health records (EHRs) between different healthcare providers and systems, allowing for better patient care and coordination of care across different providers. In finance, interoperability between different banking systems is important for seamless and secure transactions between banks and financial institutions.
Interoperability is often achieved through the use of standardized communication protocols and data formats, allowing different systems to understand and interpret data in a consistent way. Standardization also ensures that different systems can work together without the need for complex custom integrations or middleware.
Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin halving is an event that occurs approximately every four years on the Bitcoin blockchain. During this event, the reward for mining a new block is cut in half. The purpose of this event is to control the inflation of Bitcoin and limit the supply of new Bitcoin that is introduced into circulation.
The first Bitcoin halving occurred in 2012, reducing the block reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. The second halving occurred in 2016, reducing the block reward from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC. The third halving occurred in 2020, reducing the block reward from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC.

The impact of halving events on the price of Bitcoin is a subject of much debate and speculation. Some analysts argue that the reduction in the supply of new Bitcoin will increase the value of existing Bitcoin, while others argue that the impact of halving events on the price of Bitcoin is minimal and that other factors, such as investor sentiment and market demand, have a much greater impact on the price of the cryptocurrency.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are digital forms of fiat currencies issued by a country’s central bank. They are designed to be used for digital payments and transactions, just like physical currency. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, CBDCs are issued and regulated by the government, and their value is backed by the central bank.
CBDCs can come in two forms: a retail CBDC and a wholesale CBDC. A retail CBDC is designed for use by the general public and is meant to replace physical currency. A wholesale CBDC is designed for use by financial institutions and is used to facilitate large-value transactions between banks and other financial institutions.

The implementation of CBDCs could have several benefits, including increased efficiency and speed of transactions, reduced transaction costs, increased financial inclusion, and improved control over money supply and monetary policy.
Several countries, including China, Sweden, and the Bahamas, have already launched pilot programs for CBDCs, while others such as the United States and the European Union are exploring the possibility of issuing CBDCs.
Global Economic Uncertainty
Global economic uncertainty refers to a state of instability and unpredictability in the global economy, characterized by a lack of clarity and confidence about the future economic outlook. This can arise from a variety of factors, such as political instability, economic policy changes, trade tensions, natural disasters, or global health crises, among others.
When there is uncertainty in the global economy, businesses, investors, and consumers may become hesitant to make investments or purchases, leading to a slowdown in economic activity. This can also lead to increased volatility in financial markets, as investors try to navigate the uncertain environment.
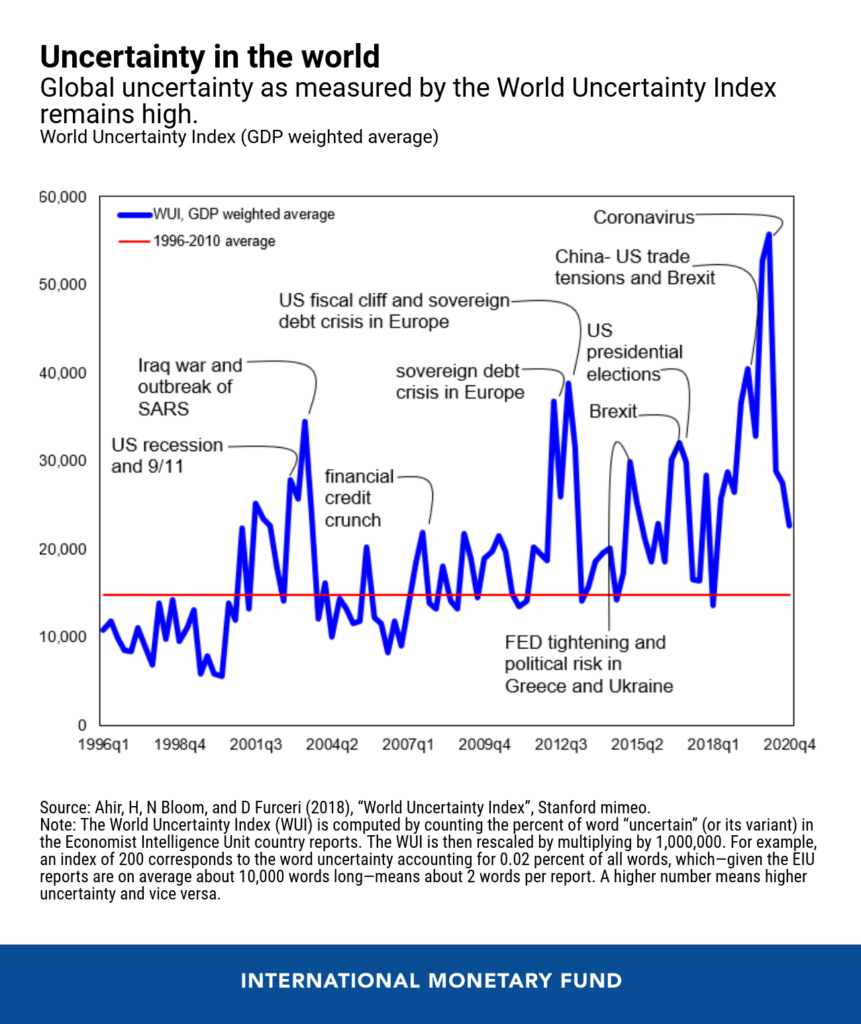
Governments and central banks often respond to economic uncertainty by implementing policies aimed at stabilizing the economy, such as fiscal stimulus, monetary policy adjustments, or regulatory changes. However, the effectiveness of these policies can vary depending on the nature and severity of the uncertainty.
Overall, global economic uncertainty can have significant implications for businesses, individuals, and governments, highlighting the importance of staying informed and adapting to changing economic conditions.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements refer to the developments, innovations, and improvements in technology that have occurred over time. These advancements have transformed the way we live, work, communicate, and even think. Some of the major technological advancements that have occurred over the years include:

- The internet: The internet has revolutionized the way we communicate, access information, and do business. It has made the world a smaller place by connecting people from different parts of the world.
- Mobile devices: Mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets have become an integral part of our lives. They have transformed the way we communicate, entertain ourselves, and even do business.
- Artificial intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform many industries, from healthcare to finance to manufacturing. AI has the ability to learn, adapt, and make decisions on its own.
- Renewable energy: Advances in renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, have the potential to transform the way we produce and consume energy. These technologies offer a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
- 3D printing: 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing by allowing for the creation of complex products with less waste and more customization.
- Robotics: Advances in robotics have led to the development of robots that can perform complex tasks, such as surgery and space exploration.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology has the potential to transform many industries by offering a more secure and transparent way of recording and storing data.
These are just a few examples of the many technological advancements that have occurred over the years. As technology continues to advance, it will likely have an even greater impact on our lives and the world around us.